
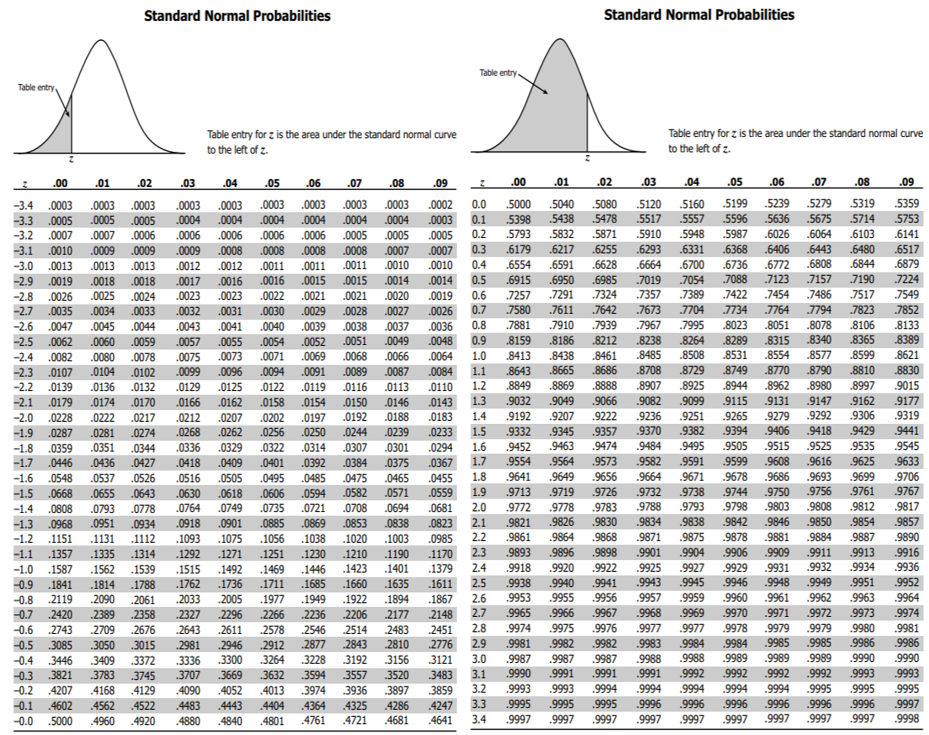
The normal distribution table for right-tailed test is given below. The t table for two tail probability is given below. Given a specified value for : For a two- sided test, find the column corresponding to 1-/2 and reject the null hypothesis if the absolute value of the test statistic is greater than the value of t1-/2, in the table below. In this case, the t critical value is 2.132. Due to the symmetry of the t distribution, we only tabulate the positive critical values in the table below. Pick the value occurring on the intersection of mentioned row and column.
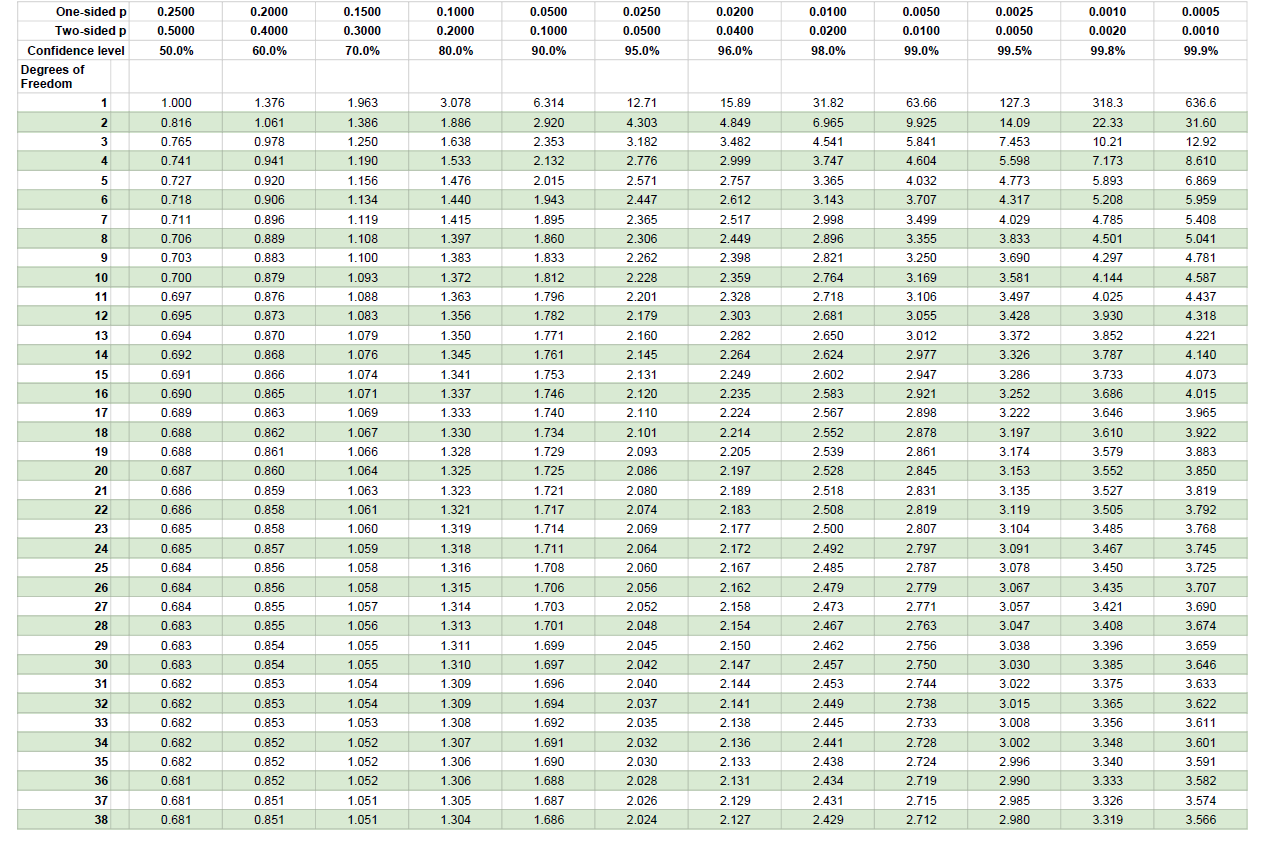
Also look for the significance level α in the top row. The table given below works as a critical t value calculator. T critical value calculator is used to calculate the critical value of t using a degree of freedom and significance level alpha. The T distribution is also known as the 'student t distribution'. Look for the degree of freedom in the most left column. It is symmetrical, bell-shaped, and similar to the standard normal curve. Standard Normal Cumulative Probability Table Cumulative probabilities for POSITIVE z-values are shown in the following table: Title: std normal table. We should use Table E (the standard normal table) or Table F (using the bottom row of the t distribution, which is equivalent to a standard normal distribution) to find the critical value. Let’s assume that the test value has a standard normal distribution. For example, the area to the left of z 1.09 is given in the table as. that we know (like the standard normal or t distribution). Since the total area under the bell curve is 1 (as a decimal value which is equivalent to 100), we subtract the area from the table from 1. Subtract 1 from the sample size to get the degree of freedom.ĭepending on the test, choose one tailed t distribution table or two tailed t table below. To find the area to the right of a positive z-score, begin by reading off the area in the standard normal distribution table. However, if you want to find critical values without using t table calculator, follow the examples given below.įind the t critical value if size of the sample is 5 and significance level is 0.05. The t distribution table (student t test distribution) consists of hundreds of values, so, it is convenient to use t table value calculator above for critical values. U is the quantile function of the normal distribution,Ĭritical value of t calculator uses all these formulas to produce exact critical values needed to accept or reject a hypothesis.Ĭalculating critical value is a tiring task because it involves looking for values into t distribution chart. In the table of the standard normal () distribution, an area of 0.475 corresponds to a value of 1.96. The region to the left of and to the right of 0 is 0.5 0.025, or 0.475. Each of the shaded tails in the following figure has an area of 0.025. Q t is the quantile function of t student distribution, A 95 degree confidence corresponds to 0.05.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
